U.S. consumers are struggling with dangerously high debt levels. As of Q2 2024, household debt reached a record $17.8 trillion, marking a $109 billion increase from the previous quarter. The rising debt is a key indicator of the ongoing financial stress felt by Americans, exacerbated by post-COVID price hikes and stagnant incomes.
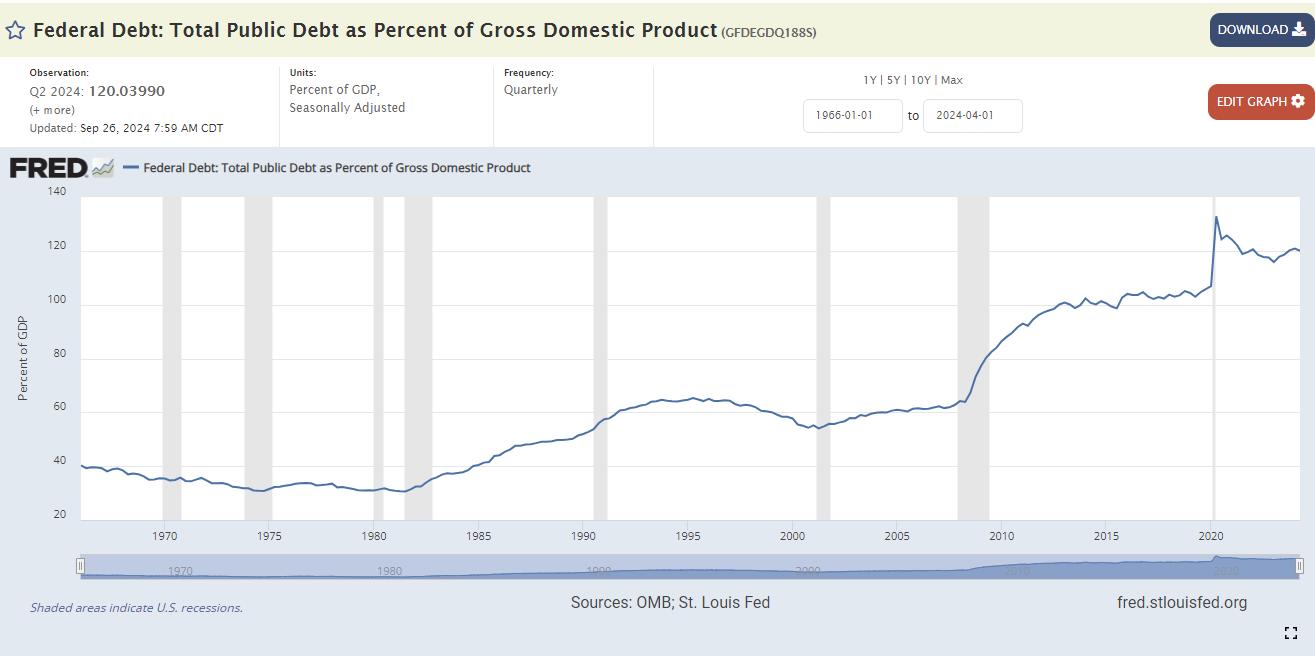
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio: The U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio for 2024 is 120.04%, reflecting the nation’s growing financial obligations. This ratio, measuring national debt against economic output, points to significant challenges in sustaining government borrowing.
- Consumer Credit: Credit card debt alone rose by $27 billion, hitting $1.14 trillion, while auto loan balances increased by $10 billion to reach $1.63 trillion. These figures highlight a troubling trend of increasing consumer borrowing, pushing debt-to-income ratios to unsustainable levels.
While the U.S. economy shows signs of recovery, with inflation cooling to below 3% and interest rate cuts in September, the financial burden on households remains heavy. With income growth lagging behind price increases, many Americans are finding it increasingly difficult to keep up with debt, raising questions about long-term economic stability.
Sources:
- Federal Reserve Board – Household Debt Overview
- Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis – Debt-to-GDP Ratio
- Federal Reserve Bank of New York – Quarterly Report on Household Debt and Credit
- Pew Research Center – Long-term Financial Impact of COVID-19
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau – Early Effects of COVID-19 on Consumer Credit