I would like to review a few items this morning:
- Commercial deposit withdrawals
- Bank Term Funding Program (BTFP) making up for gaps
- Todays notice from FDIC banks aren’t correctly reporting the amount of deposits they have that aren’t covered by federal insurance*.
\When banks incorrectly report uninsured deposits, it could create a perception in the market that these banks are more stable than they actually are.)
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/20230721/
https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/DPSACBW027SBOG
A tad over a year ago (4/13/2022) the high was hit at $18,158.3536 billion
| Date | Deposits, All Commercial Banks (billions) | Down from all time high (billions) |
|---|---|---|
| 4/13/2022 | $18,158 | 0 |
| 2/22/2023 (Run picks up speed) | $17,690 | -$468 billion |
| 3/1/2023 | $17,662 | -$496 billion |
| 3/8/2023 | $17,599 | -$559 billion |
| 3/15/2023 | $17,428 | -$730 billion |
| 3/22/2023 | $17,256 | -$902 billion |
| 3/29/2023 | $17,192 | -$966 billion |
| 4/5/2023 | $17,253 | -$905 billion |
| 4/12/2023 | $17,168 | -$990 billion |
| 4/19/2023 | $17,180 | -$978 billion |
| 4/26/2023 | $17,164 | -$994 billion |
| 5/3/2023 | $17,149 | -$1,009 billion |
| 5/10/2023 | $17,123 | -$1,035 billion |
| 5/17/2023 | $17,152 | -$1006 billion |
| 5/24/2023 | $17,238 | -$920 billion |
| 5/31/2023 | $17,282 | -$876 billion |
| 6/7/2023 | $17,203 | -$955 billion |
| 6/14/2023 | $17,297 | -$861 billion |
| 6/21/2023 | $17,343 | -$815 billion |
| 6/28/2023 | $17,342 | -$816 billion |
| 7/5/2023 | $17,367 | -$791 billion |
| 7/12/2023 | $17,289 | -$869 billion |
All this money pulled from commercial banks as M2 (U.S. money stock–currency and coins held by the non-bank public, checkable deposits, and travelers’ checks, plus savings deposits, small time deposits under 100k, and shares in retail money market funds) is decreasing:
https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/M2SL
A little less than a year ago (July 2022) the M2 high was hit at $21,703 billion
| Date | M2 (billions) | Down from all time high (billions) |
|---|---|---|
| July 2022 | $21,703 | 0 |
| August 2022 | $21,660 | -$43 billion |
| September 2022 | $21,524 | -$179 billion |
| October 2022 | $21,432 | -$271 billion |
| November 2022 | $21,398 | -$305 billion |
| December 2022 | $21,358 | -$345 billion |
| January 2023 | $21,212 | -$491 billion |
| February 2023* | $21,076 | -$627 billion |
| March 2023 | $20,840 | -$863 billion |
| April 2023 | $20,673 | -$1030 billion |
| May 2023 | $20,805 | -$898 billion |
\Bank run in commercial banks picked up in February 2023.)
So how are they getting money? They sure as heck are not lending:
Commercial and Industrial (C&I) loans are loans made to businesses or corporations, not to individual consumers. These loans can be used for a variety of purposes, including capital expenditures (like buying equipment) and providing working capital for day-to-day operations. They are typically short-term loans with variable interest rates 1.
C&I loans are a key driver of economic growth because they provide businesses with the funds they need to expand, invest, and hire, which can stimulate economic activity. They are a major line of business for many banking firms as they provide credit for a wide array of business purposes 2.
As interest rates have risen, it has becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money. This increased cost can be passed on to businesses in the form of higher interest rates on commercial and industrial loans. This means that businesses would have to pay more to borrow money, which would make them less likely to take out loans for things like expansion or equipment upgrades–lining up with the recent downturn we can observe:
https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/BUSLOANS
Commercial and Industrial Loans hit a recent high in January of 2023. ($2,815 billion)
| Date | Commercial and Industrial Loans, All Commercial Banks ($ billions) | Down from all time high (billions) |
|---|---|---|
| May 2022 | $2,613 | – |
| June 2022 | $2,675 | – |
| July 2022 | $2,707 | – |
| August 2022 | $2,730 | – |
| September 2022 | $2,752 | – |
| October 2022 | $2,778 | – |
| November 2022 | $2,795 | – |
| December 2022 | $2,807 | – |
| January 2023 | $2,815 | 0 |
| February 2023* | $2,807 | -$8 billion |
| March 2023 | $2,795 | -$20 billion |
| April 2023 | $2,774 | -$41 billion |
| May 2023 | $2,767 | -$48 billion |
| June 7, 2023 | $2,752 | -$63 billion |
| June 14, 2023 | $2,765 | -$50 billion |
| June 21, 2023 | $2,762 | -$53 billion |
| June 28, 2023 | $2,754 | -$61 billion |
| July 5, 2023 | $2,755 | -$60 billion |
| July 12, 2023 | $2,752 | -$63 billion |
Borrowing from the liquidity fairy is spiraling to make up for it shrinking M2 and dwindling deposits:
- Bank Term Funding Program (BTFP)
- Discount Window/Primary Credit
- “Other Credit Extensions”
Bank Term Funding Program (BTFP):
https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/H41RESPPALDKNWW
| Date | Bank Term Funding Program (BTFP) | Up from 3/15, 1st week of program ($ billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 3/15 | $11.943 billion | $0 billion |
| 3/22 | $53.669 billion | $41.723 billion |
| 3/29 | $64.403 billion | $52.460 billion |
| 3/31 | $64.595 billion | $52.652 billion |
| 4/5 | $79.021 billion | $67.258 billion |
| 4/12 | $71.837 billion | $59.894 billion |
| 4/19 | $73.982 billion | $62.039 billion |
| 4/26 | $81.327 billion | $69.384 billion |
| 5/3 | $75.778 billion | $63.935 billion |
| 5/10 | $83.101 billion | $71.158 billion |
| 5/17 | $87.006 billion | $75.063 billion |
| 5/24 | $91.907 billion | $79.964 billion |
| 5/31 | $93.615 billion | $81.672 billion |
| 6/7 | $100.161 billion | $88.218 billion |
| 6/14 | $101.969 billion | $90.026 billion |
| 6/21 | $102.735 billion | $90.792 billion |
| 6/28 | $103.081 billion | $91.138 billion |
| 7/5 | $101.959 billion | $90.016 billion |
| 7/12 | $102.305 billion | $90.362 billion |
| 7/19 | $102.927 billion | $90.984 billion |

- Association, or credit union) or U.S. branch or agency of a foreign bank that is eligible for primary credit (see 12 CFR 201.4(a)) is eligible to borrow under the Program.
- Banks can borrow for up to one year, at a fixed rate for the term, pegged to the one-year overnight index swap rate plus 10 basis points.
- Banks have to post collateral (valued at par!).
- Any collateral has to be “owned by the borrower as of March 12, 2023.”
- Eligible collateral includes any collateral eligible for purchase by the Federal Reserve Banks in open market operations.
Richard Ostrander (one of the architects of BTFP) spoke about it the other day:
Discount Window/Primary Credit:
https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/WLCFLPCL
| Date | Discount Window | Down from 3/15 high |
|---|---|---|
| 3/15 | $152.853 billion | $0 billion |
| 3/22 | $110.248 billion | -$42.605 billion |
| 3/29 | $88.157 billion | -$64.696 billion |
| 4/5 | $69.705 billion | -$83.148 billion |
| 4/12 | $67.633 billion | -$85.22 billion |
| 4/19 | $69.925 billion | -$82.928 billion |
| 4/26 | $73.855 billion | -$78.998 billion |
| 5/3 | $.5345 billion | -$152.3185 billion |
| 5/10 | $.9323 billion | -$151.9207 billion |
| 5/17 | $.9048 billion | -$151.9482 billion |
| 5/24 | $.4211 billion | -$152.4319 billion |
| 5/31 | $.3971 billion | -$152.4559 billion |
| 6/7 | $.3167 billion | -$152.5363 billion |
| 6/14 | $.3618 billion | -$152.4912 billion |
| 6/21 | $.3208 billion | -$152.5322 billion |
| 6/28 | $.3209 billion | -$152.5321 billion |
| 7/5 | $.3356 billion | -$152.5174 billion |
| 7/12 | $.2682 billion | -$152.5848 billion |
| 7/19 | $.2633 billion | -$152.5897 billion |
Primary Credit allows banks to borrow against collateral at the current federal funds rate:

Overview:
Federal Reserve lending to depository institutions (the “discount window”) plays an important role in supporting the liquidity and stability of the banking system and the effective implementation of monetary policy.
By providing ready access to funding, the discount window helps depository institutions manage their liquidity risks efficiently and avoid actions that have negative consequences for their customers, such as withdrawing credit during times of market stress. Thus, the discount window supports the smooth flow of credit to households and businesses. Providing liquidity in this way is one of the original purposes of the Federal Reserve System and other central banks around the world.
The “Primary Credit” program is the principal safety valve for ensuring adequate liquidity in the banking system. Primary credit is priced relative to the FOMC’s target range for the federal funds rate and is normally granted on a “no-questions-asked,” minimally administered basis. There are no restrictions on borrowers’ use of primary credit.
Examples of common borrowing situations:
- Tight money markets or undue market volatility
- Preventing an overnight overdraft
- Meeting a need for funding, including a short-term liquidity demand that may arise from unexpected deposit withdrawals or a spike in loan demand
The introduction of the primary credit program in 2003 marked a fundamental shift – from administration to pricing – in the Federal Reserve’s approach to discount window lending. Notably, eligible depository institutions may obtain primary credit without exhausting or even seeking funds from alternative sources. Minimal administration of and restrictions on the use of primary credit makes it a reliable funding source. Being prepared to borrow primary credit enhances an institution’s liquidity.
Notice how use of the Discount Window has PLUMMETED as BTFP has come in to play?
BTFP offers higher interest rates now but longer terms–to need over $100 billion in liquidity at over 5.5% interest must really be all about ‘surviving another day’?
“Other credit extensions”:
https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/WLCFOCEL
| Date | Other Credit Extension | Up from 3/15, 1st week of program ($ billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 3/15 | $142.8 billion | $0 billion |
| 3/22 | $179.8 billion | $37 billion |
| 3/29 | $180.1 billion | $37.3 billion |
| 4/5 | $174.6 billion | $31.8 billion |
| 4/12 | $172.6 billion | $29.8 billion |
| 4/19 | $172.6 billion | $29.8 billion |
| 4/26 | $170.3 billion | $27.5 billion |
| 5/3 | $228.2 billion | $85.4 billion |
| 5/10 | $212.5 billion | $69.7billion |
| 5/17 | $208.5 billion | $65.7 billion |
| 5/24 | $192.6 billion | $49.8 billion |
| 5/31 | $188.092 billion | $45.292 billion |
| 6/7 | $185.162 billion | $42.4 billion |
| 6/14 | $180.468 billion | $37.7 billion |
| 6/21 | $172.342 billion | $29.542 billion |
| 6/28 | $168.293 billion | $25.493 billion |
| 7/5 | $164.775 billion | $21.955 billion |
| 7/12 | $162.438 billion | $19.638 billion |
| 7/19 | $159.640 billion | $16.84 billiom |
“Other credit extensions” includes loans that were extended to depository institutions established by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). The Federal Reserve Banks’ loans to these depository institutions are secured by collateral and the FDIC provides repayment guarantees.
How I understand this works:
- The FDIC created temporary banks to support the operations of the ones they have taken over.
- The FDIC did not have the money to operate these banks.
- The Fed is providing that in the form of a loan via “Other credit extensions”.
- The FDIC is going to sell the taken over banks assets.
- Whatever the difference between the sale of the assets and the ultimate loan number is, will be the amount split up amongst all the remaining banks and applied as a special fee to make the Fed ‘whole’.
- It can be argued the consumer will ultimately end up paying for this as banks look to pass this cost on in some way.
There has been an update on this piece back in May:
Whatever the difference between the sale of the assets and the ultimate loan number is, will be the amount split up amongst all the remaining banks and applied as a special fee to make the Fed ‘whole’.

The Fed has created an emergency backstop program so that banks won’t have to sell assets into the market if customers pull deposits in search of more attractive yields for their savings….
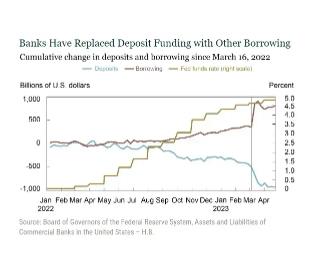
Over the few weeks prior to the FDIC receivership announcements on March 10 and 12, the banking sector lost another approximately $450 billion. Throughout, the banking sector has offset the reduction in deposit funding with an increase in other forms of borrowing which has increased by $800 billion since the start of the tightening.
The right panel of the chart below summarizes the cumulative change in deposit funding by bank size category since the start of the tightening cycle through early March 2023 and then through the end of March. Until early March 2023, the decline in deposit funding lined up with bank size, consistent with the concentration of deposits in larger banks. Small banks lost no deposit funding prior to the events of late March. In terms of percentage decline, the outflows were roughly equal for regional, super-regional, and large banks at around 4 percent of total deposit funding:
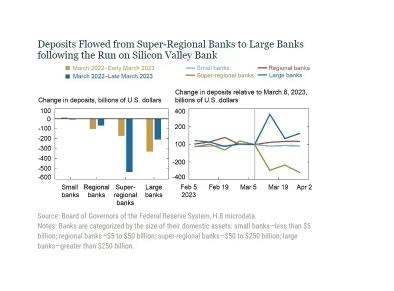
The blue bar in the left panel above shows that the pattern changes following the run on SVB. The additional outflow is entirely concentrated in the segment of super-regional banks. In fact, most other size categories experience deposit inflows.
The right panel illustrates that outflows at super-regionals begin immediately after the failure of SVB and are mirrored by deposit inflows at large banks in the second week of March 2022.
Further, while deposit funding remains at a lower level throughout March for super-regional banks, the initially large inflows mostly reverse by the end of March. Notably, banks with less than $100 billion in assets were relatively unaffected.

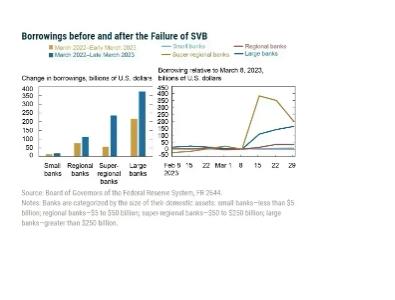
- Large banks increased borrowing the most, which is in line with deposit outflows being strongest for larger banks before March 2023.
- During March 2023, both super-regional and large banks increase their borrowings, with most increases being centered in the super-regional banks that faced the largest deposit outflows.
- Note, however, that not all size categories face deposit outflows but that all except the small banks increase their other borrowings.
- This pattern suggests demand for precautionary liquidity buffers across the banking system, not just among the most affected institutions:
Wut Mean?
- Banks have been replacing deposit outflows with the borrowing we have covered above.
- ‘Strong and resilient’ indeed….
- It is starting to smell idiosyncratic all up in here:
https://www.marketwatch.com/story/u-s-bank-lending-falls-in-latest-week-fed-says-b633e731
To me, this is looking more and more like over-reliance on Central Bank Funding!
As banks seem to be relying on these programs as a regular source of funding, it will lead to several issues:
- Moral Hazard: Banks might take on more risk than they would otherwise, knowing they have a safety net in the form of cheap funding from the central bank.
- This could lead to riskier lending and investment practices, potentially setting the stage for future financial instability.
- Distorted Market Signals: In a healthy market, interest rates and other signals help guide banks’ lending and investment decisions. But if banks can always access cheap funding from the central bank, they might ignore these signals. This could lead to an inefficient allocation of resources, with too much credit going to certain sectors and not enough to others–current AI bubble anyone?
- Reduced Market Discipline: In normal circumstances, banks should be disciplined by the market: if they take on too much risk, they should face higher funding costs or even risk bankruptcy. But if banks can always rely on central bank funding, this market discipline could be weakened, potentially leading to excessive risk-taking…
Interestingly, today FDIC observed some institutions incorrectly reduced the amount reported to the extent the uninsured deposits are collateralized by pledged assets; this is incorrect as the existence of collateral has no bearing on the portion of a deposit that is covered by federal deposit insurance!
Wut mean?:
- When banks incorrectly report uninsured deposits, it could create a perception in the market that these banks are more stable than they actually are.
- Banks that incorrectly report uninsured deposits might face liquidity challenges in extreme circumstances, where depositors simultaneously demand their funds.
- The FDIC noticed that some banks aren’t correctly reporting the amount of deposits they have that aren’t covered by federal insurance. Some banks mistakenly think that if a deposit is backed by assets (like collateral), it doesn’t need to be reported as uninsured.
- This isn’t right! The deposit’s status doesn’t change just because it has collateral.
- Also, some banks were leaving out deposits made by their own subsidiary companies.
TLDRS:
- Folks have pulled $869 billion in deposits since 4/13/2022
- Folks have pulled $401 billion in deposits since 2/22/2023
- Folks have pulled $78 billion in deposits in the last week.
- Today, the FDIC noticed that some banks aren’t correctly reporting the amount of deposits they have that aren’t covered by federal insurance. Some banks mistakenly think that if a deposit is backed by assets (like collateral), it doesn’t need to be reported as uninsured.
- This isn’t right! The deposit’s status doesn’t change just because it has collateral.
- When banks incorrectly report uninsured deposits, it could create a perception in the market that these banks are more stable than they actually are.
- Banks that incorrectly report uninsured deposits might face liquidity challenges in extreme circumstances, where depositors simultaneously demand their funds.
- How did all these banks pass those ‘Stress tests’ the other day needing all this liquidity and now knowing from FDIC they have accounted for uninsured deposits incorrectly?
- Reminder, while banks have the liquidity fairy, ‘we’ get the promise of 2 more rate hikes this year, Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic yet again enrichens himself inappropriately from his position.
- To fix one end of their mandate (price stability) from the inflation problem they created, the Fed will continue sacrificing employment (the other end of their mandate) to bolster price stability by continuing to raise interest rates–causing further stress businesses and households.
- I believe inflation is the match that has been lit that will light the fuse of our rocket.
90 views